How to fix PC Crashing: Troubleshooting Guide
When a computer crashes, it can disrupt your work and lead to data loss. To address this, a thorough troubleshooting process is essential. This process involves checking for hardware malfunctions which can contribute to system instability. By inspecting components like the RAM, hard drive, and cooling system, one can often pinpoint the issue.
Fixing a Windows PC requires a systematic approach. Users can utilize built-in diagnostic tools to assess and rectify problems that lead to crashes. Regular system updates, driver verifications, and malware scans are part of routine maintenance that can prevent future system crashes.
Diagnosing and Fixing Computer Crashes: A Quick Guide
Understanding the Crash
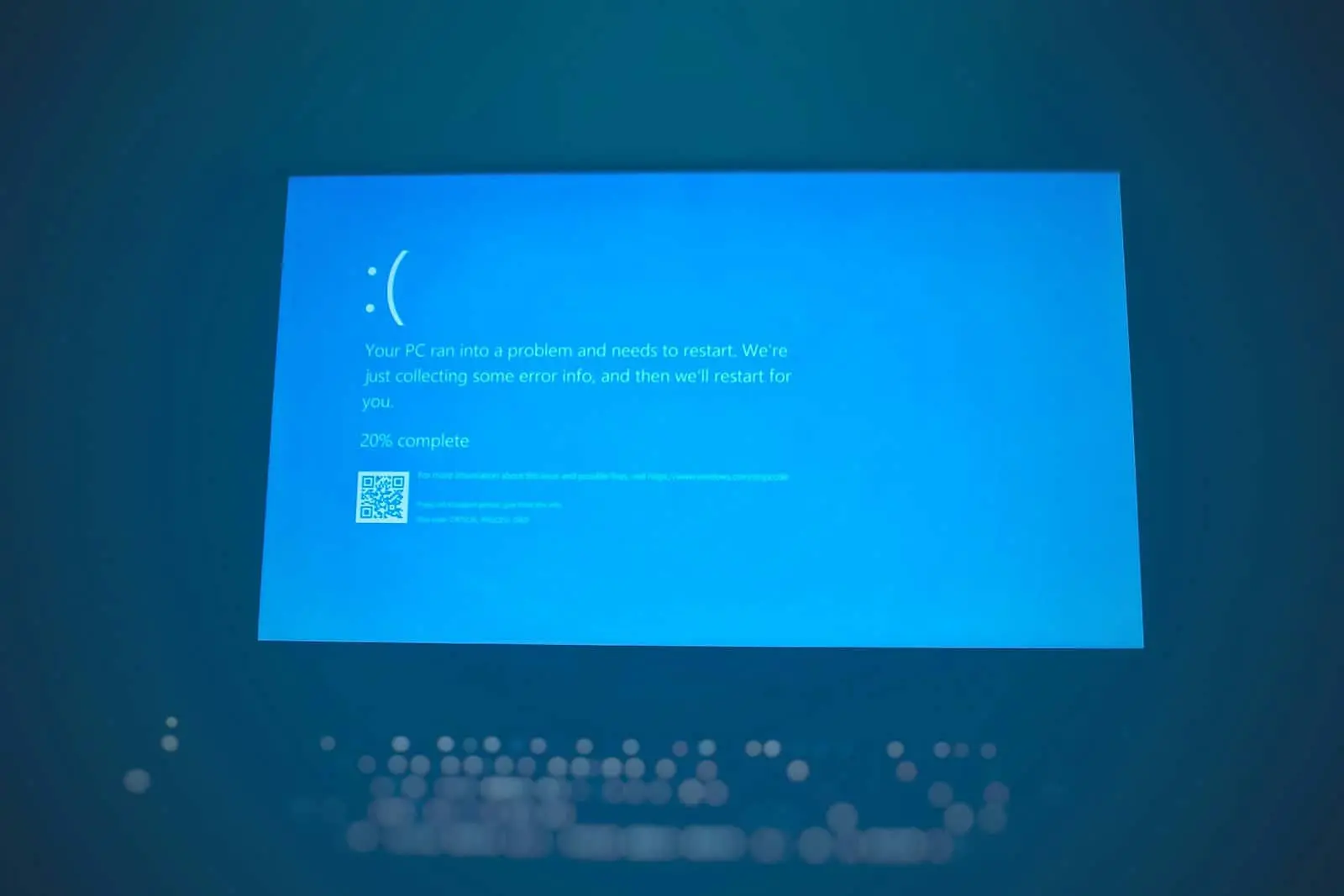
Crashes manifest in various ways, from sudden shutdowns to the dreaded blue screen. Pinpointing the type of crash helps diagnose the problem.
Different Types of Crashes:
- Sudden Shutdowns: The PC abruptly powers off without warning.
- Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): A blue screen with error codes appears.
- Freezes: The system becomes unresponsive.
- Reboots: The PC unexpectedly restarts.

Common Causes of Crashes and Solutions
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overheating | Clean dust from vents and fans. Ensure proper airflow around the PC. Check for faulty fans and replace if needed. Apply new thermal paste to the CPU if comfortable. |
| Hardware Issues | Check RAM for errors using Windows Memory Diagnostic or MemTest86. Monitor hard drive health using S.M.A.R.T. tools or CrystalDiskInfo. Ensure all connections (cables, cards) are secure. |
| Driver Problems | Update drivers for graphics card, network adapter, and other peripherals. Check for driver conflicts in Device Manager. Roll back to a previous driver version if a recent update caused issues. |
| Software Conflicts | Uninstall recently installed programs or updates that might be causing instability. Perform a clean boot to isolate problematic software. Check for malware or viruses using reputable security software. |
| Operating System Issues | Run System File Checker (SFC) to scan and repair system files. Update Windows to the latest version. Consider a system restore to a previous stable point. Reinstall Windows as a last resort. |
When to Seek Professional Help
If troubleshooting steps fail to resolve the crashes, it’s time to consult a professional. They can diagnose complex hardware issues, repair or replace components, and perform advanced software troubleshooting.
Remember:
Always back up important data regularly to prevent loss in case of a crash.
Key Takeaways
- Addressing computer crashes begins with hardware checks and system diagnostics.
- Built-in Windows tools can assist in troubleshooting and fixing crashes.
- Preventative maintenance is crucial for ongoing computer health and stability.
Diagnosing and Resolving Hardware Issues
When a computer crashes, it’s often due to hardware problems. This section guides you through checking the hardware, testing the memory and storage for errors, and handling overheating.
Checking Physical Components
It is crucial to ensure all hardware components are properly connected and functioning. Start by turning off the computer and unplugging it. Open the case and check for loose cables or connections. Push the connectors firmly into their slots. Look at the power supply to confirm it’s working. An unstable power supply can cause crashes. Inspect the graphics card and RAM to ensure they are seated properly. Dust can cause issues too, so clean dust from fans and components carefully.
Testing RAM and Hard Drive Integrity
Faulty RAM or a failing hard drive can lead to system crashes. To test the RAM, use Windows Memory Diagnostic or a third-party tool like MemTest86. These tools run before the operating system starts and can detect memory issues. For the hard drive, run the Check Disk utility. Press Windows + R, type “cmd,” and hit Enter to open Command Prompt. Type “chkdsk” followed by the drive letter to check hard disk integrity.
Managing Overheating Issues
Overheating can cause a PC to crash unexpectedly. Ensure that the internal fans are running and not obstructed. Use a program to monitor the temperature of the CPU and GPU. If the computer is often hot, improve ventilation by rearranging its position or adding more fans. Replace old thermal paste on the CPU and GPU to help with heat transfer. Regularly cleaning out dust helps prevent overheating and keeps hardware in good condition.



